Unemployment is very long term it is on individual families & entire economies. One of the several types of unemployment, the cyclical employment stands out from the broader as well as labor market dynamics. Knowing what cyclical unemployment is, its causes, its effects can provide information about the economic conditions which affect jobs. In this full article, we are going to clarify what cyclical unemployment is, what is the main distinction to make with other kind of unemployment, are contributing the factors to the cyclical unemployment, how can stop this cyclical unemployment.
What is Cyclical Unemployment?
Cyclical unemployment is when the level of unemployment increases because of the economic downturns of the recession. It is one of the main type of unemployment and is mostly related to economic business cycles fluctuations. In other words, Cyclical unemployment happens when if there is a slowdown in the economy and produces a decrease in the demand for goods and services. As consumer spending continues to fall for businesses there may be a contraction of their workforce, which may involve layoffs and job losses.
This species of unemployment is temporary and often is reversed when the economy will recover and it enters a period of expansion. You have to recognize that cyclical unemployment is not the worker’s fault in terms of his or her skills, abilities or work habits. It is all about the overall condition of the economy.
Cyclical Unemployment vs. Other Types of Unemployment
It is important to distinguish cyclical unemployment from other types of unemployment to understand its specific characteristics. Unemployment is often categorized into several different types:
| Type of Unemployment | Definition | Causes | Duration |
| Cyclical Unemployment | Unemployment caused by a decrease in demand for goods and services due to an economic downturn. | Recessions, decreases in consumer confidence, and cyclical business contractions. | Short-term, temporary during recessions or slowdowns. |
| Structural Unemployment | Unemployment caused by a mismatch between workers’ skills and available jobs, often due to technological advancements or industry changes. | Technological changes, shifts in consumer preferences, outsourcing. | Long-term unless retraining occurs. |
| Frictional Unemployment | Short-term unemployment that occurs when workers are between jobs or are entering the workforce for the first time. | Job transitions, career changes, or relocation. | Short-term, often lasts weeks to months. |
| Seasonal Unemployment | Unemployment that occurs when demand for certain jobs fluctuates with the seasons. | Agriculture, tourism, construction, and retail jobs with seasonal demand. | Temporary, tied to seasonal fluctuations. |
Cyclical Unemployment Definition
The description of cyclical unemployment can be stated as:
- “Employment that has resulted in a decrease in demand for goods and services in the midst of an economic downturn and is coupled with reduced hiring, business closures, and workforce layoffs.” Cyclical joblessness is intrinsically linked to the cyclical nature of the economy.
- Cyclical unemployment is temporary. As once the economy starts to be more active again won’t all the sudden have businesses for their workers – so think businesses will need to coax back. And what this will of course do is lower the unemployment rates. This makes cyclical labour employment a very important indicator of the state of an economy as a whole.
Causes of Cyclical Unemployment
Cyclical unemployment has some contributing factors. Learning about these grounds might more deeply reveal how such a kind of joblessness functions within the complete financial system:
- Recessions: The biggest reason for cyclical joblessness is a recession. In a recession, the economy falls into a downturn, which results in the way it decreases spending by consumers, reduces production and lowers business profit. When the demand for products and services reduces, businesses may react by reaching for cost savings and often in that push save your workforce.
- Decline in Consumer Confidence: Confidence loss by consumer constitutes they cut their spending. This decline in demand can lead even more to a slowdown of the economy, which means more layoffs and hiring freeze.
- Business Cycle Slumps: The economy goes through business cycles of growth and downturn naturally. When contratiton is occurred, cyclical unemloyment generally grows up, since business can not sell deep and money not enough. As these companies try to cut their expenses, the first ones to be cut are often the employees.
- Government Policies and World Occasions: Government rules can also impact levels of cyclical unemployment. In other words, austerity measures or higher taxes can slow economic growth, and therefore result in companies laying off employees. Similarly, worldwide events such as natural disasters, pandemic type of events (COVID-19), or geopolitical chaos might break worldwide supply chain responses and lead to lower demand, making the way for additional cyclical joblessness.
- Industrial and Technological Changes: In some cases, companies in industries that are linked to cyclical business fluctuations, such as construction, retail or manufacturing, might need to lay off staff if consumer demand changes, shifts occur in technology or if they automate their processes.
The Impact of Cyclical Unemployment on the Economy
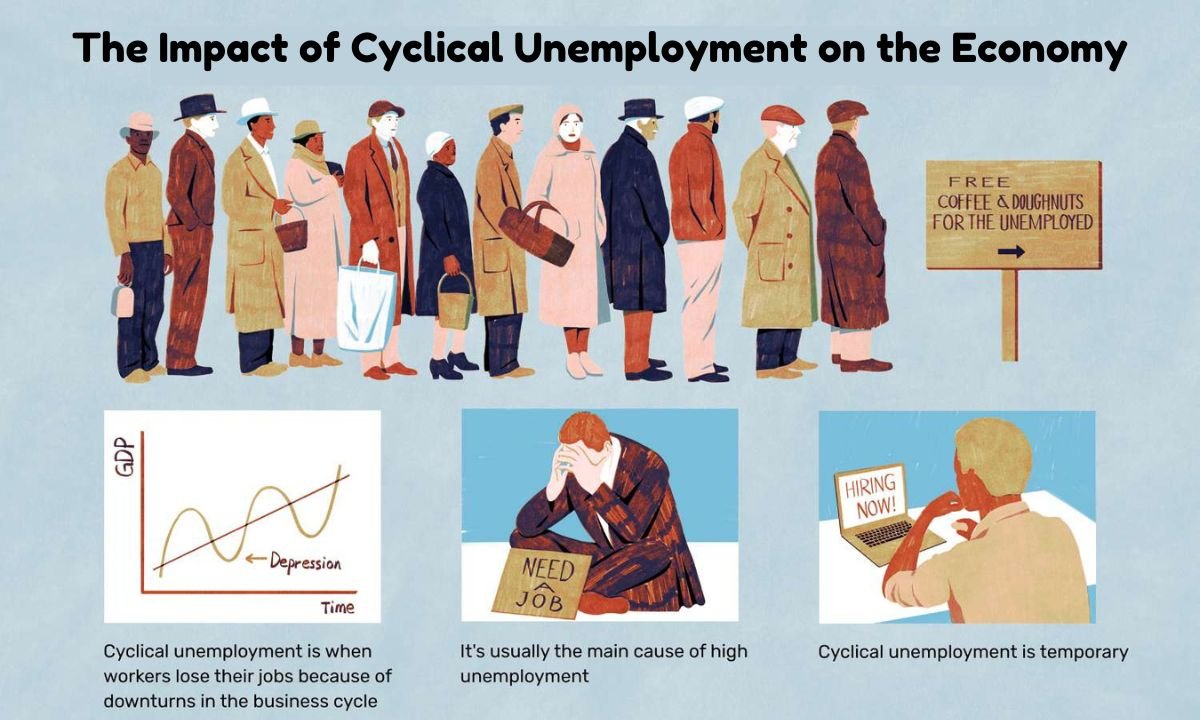
The impact of cyclical unemployment can be felt very strongly by both individuals and society in general. The economic consequences of big cyclical unemployment are:
- Economic Slowdown: When more individuals become unemployed, they maintain their status as such and thus reduce consumption. This can result in even lower demand for goods and services which can keep the economic downturn going, it creates a vicious cycle of growing unemployment and failing demand.
- Loss in Tax Revenue: With higher unemployment rates, tax revenue of government falls. This could limit the government’s capacity to finance public services and infrastructure, reducing economic growth even more.
- More Government Spending: Governments tend to take action to deal with era unemployment by raising community spending or suggesting unemployment insurance. This can partially mitigate the social consequences of unemployment but it puts excessive burden on public finances, especially in countries with high unemployment.
- Social and Psychological Consequences: Cyclical unemployment associated with elevated levels of stress, anxiety, job dissatisfaction among the workers whose employments is lost. Extended unemployment can also lead to loss of working skills which in turn makes it difficult for the individuals to rejoin the workforce when the economy starts recovering.
- Wage Competition: As more employees apply for fewer positions during an economic recession, wages may not change or even decline. This, in turn, is expected to cut consumer disposable income further, adding to a general economic downturn.
How to Combat Cyclical Unemployment
Whereas cyclical unemployment is primarily a natural outcome of the economic cycle, there are some policies that governments, businesses and employees can follow to reduce levels of it:
- Monetary and Fiscal Policies: Governments can address cyclic unemployment through the monetary and fiscal policy that boosts demand. Reducing interest rates for example makes borrowing cheaper, which leads to consumers spending more and businesses investing more. In addition, fiscal policies—raising government spending on infrastructure or as output or stimulus packages—can also raise demand and employment.
- Job Creation Programs: Governments and corporations launch job creation programs which target public works, community services, and all those sectors that have got a job for a job even in recession. These efforts can result in short-term work and assist in worker skills while economy recovers.
- Training and Reconceptualizing the Workforce: When an industry tanked, workers in those industries equipped to re-enter, retrain and reconfigure the workforce, some workers could get it back in fairly quickly. Retraining courses can empower the workers to acquire new skills and move on to industries that have huge scope, thus mitigating the deep-rooted consequences of cyclical unemployment.
- Promoting Entrepreneurship: Governments can enlist entrepreneurship through tax advantages, channels, or low-fascinating obligation. This can help spread the economy and cushion the cyclical unemployment effects on particular sectors.
Conclusion
Cyclical unemployment is an important concept to grasp for all labor market and economic condition analyses. It is seen in recessionary periods when business enterprises lower labour to cope with less consumption of goods andervice.
Also Read About 🙂 StudyKarado com