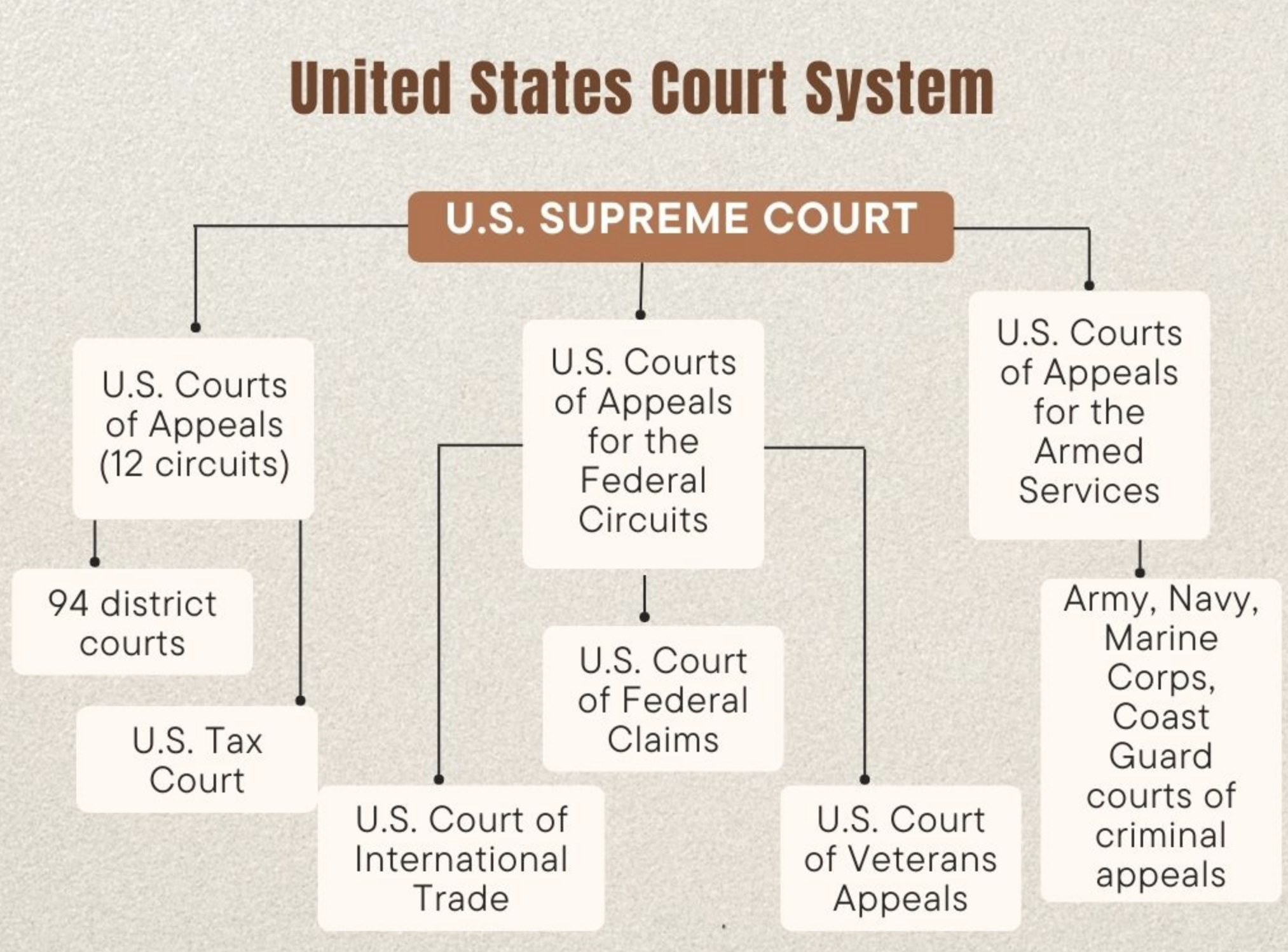
Tribal courts are a key component of the American legal structure. In Native American reservations and tribal lands, they function with a large variety of legal issues affecting tribal members and, at times, non-members. Though they may look like federal and state courts in some aspects, tribal courts are out of a different system, which includes tribal sovereignty, culture, and federal law. For people that come into play with the tribal justice system, awareness of how these courts work is very important.
Tribal Sovereignty and Legal Authority
Tribal courts base their structure on that of tribal sovereignty. Also, it is known that federally recognized tribes are, for all intents and purposes, domestic dependent nations, which have the inherent right to govern themselves. This includes the power to create courts, pass laws, and put forth regulations within their own jurisdiction. Tribal sovereignty is a pre-founding fathers issue that also is present today and is recognized through treaties, statutes, and court decisions.
Tribal courts in most cases handle issues of a civil and some criminal nature that take place on tribal lands. Also, they may try cases that involve tribal members and, at times, non-members that are involved in activity on tribal territory. Jurisdiction issues are an issue that plays out often, in which we see federal, state, and tribal authority all playing a role. It is important to know which court has what authority in a given situation before parties begin legal action.
Types of Cases Heard in Tribal Courts
Tribal courts deal with a large spectrum of issues. This may include family law issues like divorce, child custody, and adoption. Also, they look into probate issues, property disputes, contract issues, and personal injury claims that are related to tribal land. In terms of crime, tribal courts try cases that see to it that tribal members who break the law within the reservation are held accountable.
Family issues are a large component of what comes through the tribal court system. Also, it is typical for tribal courts to use tribal codes as well as culture-based principles in which they resolve domestic issues. In the case of child welfare, they see the Indian Child Welfare Act (ICWA), which plays a key role in putting forth tribal interests in the care of Native children within the state court system.
Structure of Tribal Court Systems
Tribal court systems also vary in size and structure, as do state and federal courts. Some tribes run multi-level systems that include trial and appellate courts. In other tribes a single court that deals with all issues exists. Judges may be elected, appointed, or put in place via tribal procedure. In many tribes judges are required to have legal training, which, however, varies among nations.
Procedural rules in tribal courts do indeed look to what is done in state courts, but also they are shaped to the specific culture and practice of each tribe. Some tribes also use traditional law and community-based dispute resolution techniques. In alternative dispute resolution they see mediation and peacemaking put forward to foster a harmonious and restorative approach.
The Importance of Legal Representation
In tribal courts, which is a different setting than what people are used to, they see different issues play out. Attorneys that work in these courts, in addition to knowing the basic legal principles, also have to study up on tribal codes, customs, and how federal laws play into the tribal authority.
For individuals involved in a case within the Muscogee (Creek) Nation, understanding the framework of the Creek Nation court system is particularly important. Each tribal court operates under its own laws and procedures, so reviewing relevant codes and rules can help individuals prepare effectively.
Legal in tribal courts sees tasks similar to other courts. Attorneys put together pleadings, represent clients at hearings, negotiate settlements, and give advice to clients on their rights and responsibilities. In more complex cases attorneys may address issues related to federal statutes, treaty rights, or state vs. tribe authority.
Interaction Between Tribal, State, and Federal Courts
In many cases tribal law puts forth very complex issues of which different court systems’ interaction is a large part. In some situations more than one court may assert authority. For example, a dispute that takes place on tribal land may include tribal members, non-members, or businesses within the reservation. Determining which court is to hear the case may require in-depth legal analysis.
In some cases federal courts will look at the work of tribal courts, which is usually the case when they see issues of jurisdiction or constitutional rights come up. Also, it is a general requirement by federal law that parties go through tribal court procedures first before bringing their issue to a federal court. This, in large part, is a show of respect for tribal sovereignty and the independent nature of tribal judicial systems.
Tribal courts also play a role in collaboration with state and federal agencies in issues like child welfare, public safety, and environmental regulation. They see in these intergovernmental agreements a definition of roles, which in turn promotes cooperation between entities.
Cultural Considerations in Tribal Justice
In the case of tribal courts as compared to state courts, which do so less often, it is not uncommon for tribal customs to be used in court practices. Also some tribes’ focus is on the themes of repair within the community instead of only issues of punishment. In which these tribes are concerned, for example, with how the elderly or community members at large play an element in the process, and also how traditional values play out in issues that deal with family or properties.
This cultural integration sets tribal courts apart from other judicial systems. It is an element of the larger aim to preserve tribal identity, pass down tradition, and strengthen community bonds.
Accessing Tribal Court Information
Many tribal courts post information on their rules, filing procedures, and case types to official websites and in their offices. If individuals are thinking of filing a claim or responding to a legal issue they should go over this information very carefully. Clerk staff may also give procedural advice but do not provide legal advice.
Comprehension of deadlines, filing requirements, and procedural rules is key to protecting legal interests. Also because tribal courts have unique codes in which they operate, what may apply in a state court may not in a tribal court.
Conclusion
Tribal courts play a key role in Native American self-governance. Out of sovereignty and with input from both traditional and modern legal practices, these courts serve to resolve issues for their communities, enforce laws, and protect rights. In terms of issues like family problems, civil disputes, or criminal cases, tribal courts run a separate and rich legal system.
For in the case of interaction with tribal courts, it is important that individuals are aware of their jurisdiction, procedures, and cultural setting. By this, through research and familiarization of how these courts work, parties will be better at getting through the process and at the same time fulfilling their legal responsibilities within tribal lands.