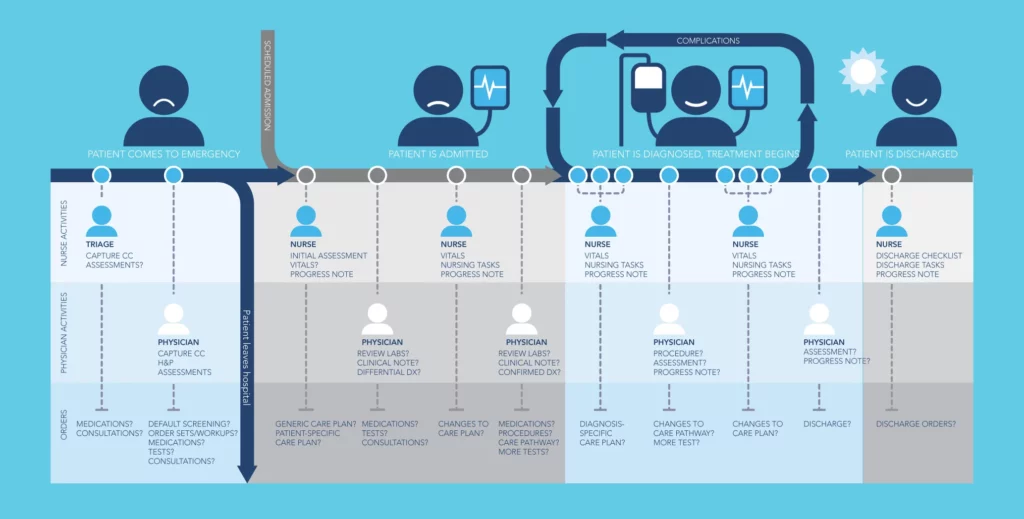
The birth of Pharma 4.0 led the industry to the idea that it should totally change its classic patient journey mapping techniques into the digital ones. Patient journey mapping has been a meaningful approach toward the achievement of improved patient outcomes because it discloses crucial facts, such as the obstacles to care delivery, patients pain points, effectiveness of patient-physician interaction, and the logic of different care-related choices. It helps in an ongoing and longitudinal representation of this data both qualitatively and quantitatively, including the action of the caregivers, patients, and HCPs.
Patient journey mapping (PJM) is also a very significant exercise that should be carried out even during the time of constructing the brand strategy to see unmet needs in the provision of care. Unmet needs determine how pharma enterprises identify growth opportunities and how to notify product positioning to payers, providers, and patients. The approach aids in the identification of barriers in existing treatment, which might range between access and adherence. The pharmaceutical businesses are then able to come up with more sophisticated interventions to avoid such challenges. PJM also enables companies to measure the effect of a disease and its treatment on care givers and patients. This assists in the identification of conditions in which the companies can develop relevant interventions that will improve the outcomes of patients.
What the Future Holds: Digital Patient Journey
With the current trend of Pharma 4.0 and the popularity of what is becoming known as emerging technologies, digital patient journey is set to grow even more in the next few years. Holistic medical provision along the patient path will be the emerging center of interest in medicine. Technology will facilitate the improvements in communication and establishing efficiencies throughout the continuum of care by making more services automated and connected in the industry.
The predictions on how technology will change healthcare in the market in the coming few years include-
- Implementation of AI- It turns out that there are unlimited opportunities where AI can be adopted; these include chronic/rare illnesses, radiology, and risk analysis. Nevertheless, to implement it, such crucial steps as patient-centered nature of the designed services and issues with data privacy should be addressed. In the following part, this article will elaborate on it further.
- Convenient and easily movable care- With the growing advancement of technology in medical gear industry, the medical equipment and sensors will be more efficient but small enough to carry around easily. Thus, the processes that were performed in laboratories will be shifted to homes.
- Interoperable health data- The desire of having a common health data exchange, standard, and regulated in cross-platforms shall be realized in the new generation of the EHR systems. Such advancements in technology as blockchain will help to build trust and heighten transparency.
- Telemedicine will change- It is terminate because Telemedicine will allow healthcare organizations to provide care at an incredibly lower cost and improve convenience and access. It will propel the same in no time with the introduction of 5G cellular communication.
- Wearable technology- wearables are evolving to not only be fitness trackers but actual medical-grade devices that can track and stream real time data to the physician and automatically enter into digital health records.
- Careful Customization- Newfound ideas in health like nanobots will be introduced so that the patient body is always monitored by them, drugs are administered to the body and all information is always relayed to the cloud where medical personnel are in close sight.
- Reality-virtuality spectrum- The aspect of using AR and VR as aids is yet to leave its mark on medical intervention and they are bound to increase in the future. Nowadays, there is certain study being conducted around the world to learn how they could be used in treatment of phobias, as a piece of therapy on the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder, pain management, etc.
The Implications of pharma: Mapping the Digital patient journey
As the digital technology is being adopted fast and more and more patients are becoming connected and well informed, it has become important that the desires and interests of the patients are made central to all healthcare decisions which are made by stakeholders in the healthcare industry.
In the pharma industry, nowadays patients are coming to be acknowledged as primary stakeholders in the healthcare discourses. The academia, physicians, payers, and regulatory associations have already begun to reinforce the decision-making process with the patient feedback. The value of self-reported outcomes has increased exponentially as well because payers have become vehement users of these outcomes when making drug-repayment-related decisions. Conversely, payers succeed in involving the patients in the health-technology assessment.
The current paradigm shift that is being experienced in pharma is patient-centered. The patient-centric culture is being embraced by many businesses as they continue with the digital- technology-led transitions to such services as beyond-the-pill.
Nevertheless, before getting to the true patient-centricity, pharma needs first to research and understand the experience, behavior, and unmet need of the patient along the care continuum. This necessitates the reassessment of pharma businesses to their concept of the patient journey and the various touch points.
So how is the digital patient journey providing a support based on the unmet needs-
- Behavioral needs: The behavior of a patient is affected by his or her surroundings, emotions, and the way treatment option are implemented. Compliance, e.g., may be a problem when the patient believes that the proposed treatment would not work. Consequently, the behavior of a patient is very essential to the success of the treatment.
- Clinical needs: On some occasions, clinical needs may lack continuity in provision and practice. The absence of knowledge about rare diseases in doctors may be one of the factors of poor diagnostics of patients with rare diseases, thus causing both psychological and physical pressure on the patient.
- Emotional needs: The patients must feel that they are heard and understood. An example of such one is an HCP displaying empathy, which would help improve the trust of a patient and improve communication. Patients that are perceived hear and listened to are more open to advise given by the doctor.
- Data needs: To deliver top-level services and make sure that consumers will get effective care at the right place at the right time, they have to access their health data. Indicatively, when a patient is not aware of the negative consequences of their treatment, then they lack knowledge on where to call upon in case of need.
Mapping the Patient Journey: Using AI in Pharma.
One of the core components of PJM is AI pharma because it can consume and analyze massive amounts of information at previously unachievable scale and velocity. The use of AI algorithms can easily pull data together that can come in various sources, such as the EHRs, the claims data, social media, wearable devices, and so on, creating a clearer and more tangible picture of what the patient has gone through.
Such is the AI way of the patient journey mapping-
- Using RWD to observe holistic information about patient experiences
- This is what AI data collection and collation of various sources will achieve.
- Segmentation of patients and sentiment analysis carried out by ML algorithms and NLP
- Predictive analytics and both detecting and performing deep learning patterns in patient data
What the pharma businesses should undertake when considering the application of the AI in their PJM-
- Locate the suitable datasets and sources of AI-driven PJM
- Create an AI infrastructure and define right algorithms to analyze data
- Keep both the data and ethical concerns in mind regarding AI-driven patient-data collection and reporting
Conclusion
The pharma sector cannot just ignore the fact that patient journey mapping is a very inevitable tool that is able to speed up progress towards becoming industry 5.0. And with the advent of the AI and big data combination, the paradigm shifts represent as the technology is providing incomparable solutions and revelations.
The interactive AI-enabled tracking maximizes the engagement strategies, and, as a result, patient care becomes effective. This people-driven approach resonates with the shift of the healthcare industry towards individual medicine. With the AI gaining its capacity to generate innovation and predictive insights, the shaping of the pharma research and healthcare may be presented as the groundwork of the future. In adopting AI and digital health, pharma will be entering the road of more success stories and satisfaction of patients.