AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism has a comprehensive and detailed curriculum. It is essential to have one-stop-shop resource that can guide you through every topic. In case you are looking for an AP Physics C Equation Sheet, then you are at the right place. In this article, we are going to explain everything included in each of the sections of the physics equation sheet. We are also going to give you a few tips on how to utilize the equation sheet most effectively. Moreover, we will show you a few examples on student-created sheets. We will kick things off with all the subsections on velocity that span the entire page of your AP Physics C Equation Sheet.
What Is AP Physics C Equation Sheet?
AP Physics C is a college-level program created to help you get ready for the AP exam. While the course places an emphasis on physical concepts, it also covers some experimental approaches. The math skills necessary for a successful test are included as well.
AP Physics C Equation Sheet
- Force = Mass x Acceleration (Newton’s Law of Motion)
- F = ma (Work-Energy Theorem)
- Work Done = Force x Distance (Work-Energy Theorem)
- Power = Work Done / Time (Work-Energy Theorem)
- Energy is the ability to do work (Equation of Energy)
- Total energy is conserved in an isolated system (Equation of Energy)
- Kinetic energy is proportional to the square of the velocity (Kinematics)
The Methods on the AP Physics C Equation Sheet and How to Apply Them
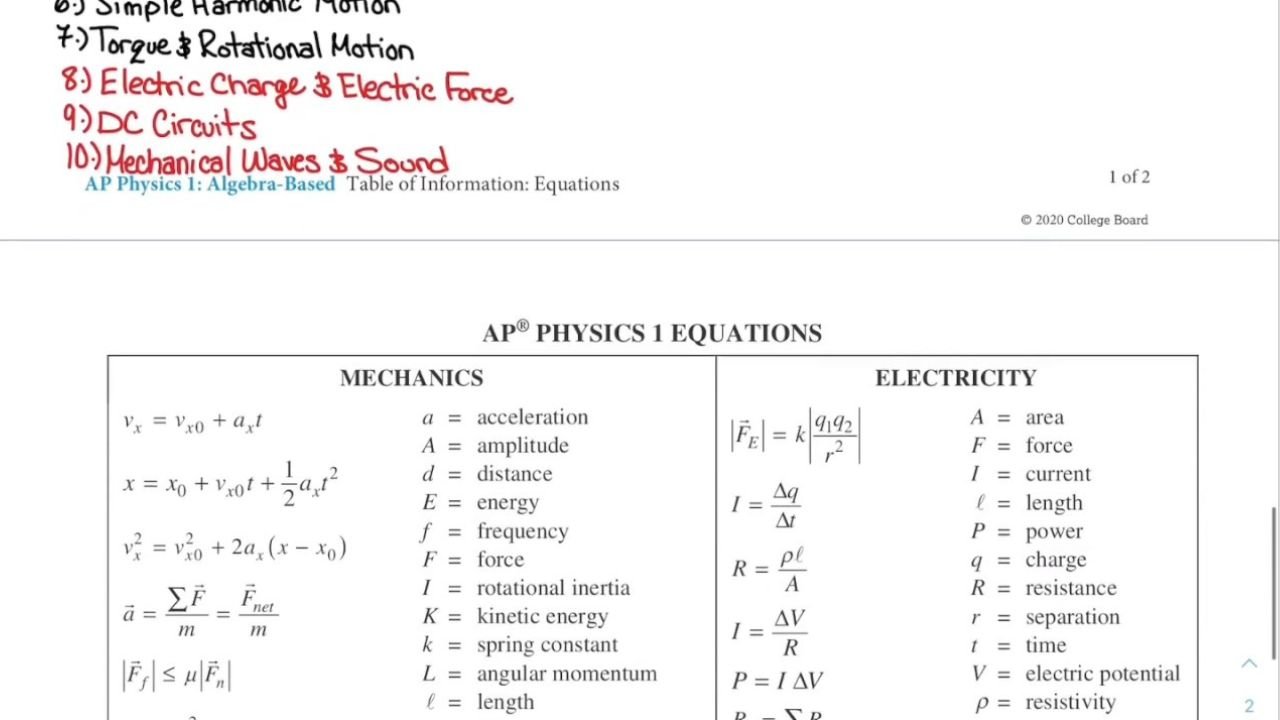
Prefixes, Constants and conversion factors; values of trigonometric functions for common angles; unit symbols and equations. These are all included in the AP Physics C formula sheet, which is divided into five sections. Let’s have a quick look at each of the major parts in further detail right below.
Prefixes, Unit Symbols, and Trigonometric Functions for Common Angles
The prefixes and unit symbols tables will come in clutch as you try to pass the AP Physics C exam. When attempting an exam question, a prefix is attached to the term for a specific unit to indicate a value or amount; such as kilo (the prefix) and grams (the unit), or Giga (the prefix) and watts (the unit). The chart of prefixes on the equation sheet can help jog your memory in case you can’t remember the figure of a certain prefix.
Constants and conversion factors
The constants and conversion factors on the AP Physics C formula sheet will be a lifesaver while carrying out various computations during the AP exam. These numbers, often known as “physical constants” or “universal constants,” are distinct in that they have the same value in any and every case in nature.
Equations
Most of the solution sheet during the AP Physics C examinations contains basic physics formulas. Mechanics, electricity and magnetism, geometry, and trigonometry are the three domains in which these equations are subdivided. A character key has been included in each part of calculations. To make you know what each figure in a given issue stands for. Although our version of the method sheet doesn’t use it, the actual method sheets for the AP Physics C exam. It does provide a brief discussion of each equation as well as how to use it for the exam.
Equations in Mechanics
The following is a list of equations that will be useful in solving problems in physics. Keep in mind that you can solve any equation by substitution, elimination, addition, or subtraction. If an equation seems difficult to solve, try to use one of these methods to simplify it.
Newton’s Second Law: The Work-Energy Theorem
The Work-Energy theorem states that the change in kinetic energy equals the work done on a system. It is as follows:
Where W is the work by a constant force F on a mass m for a displacement s along its direction of motion, called impulse (J).
Impulse is the integral of force over time; F = ∫Fdt, where F is force (N), t is time (s).
Newton’s Third Law: Forces and Acceleration
A force F acting on an object produces an acceleration according to Newton’s third law: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Equations of Electricity and Magnetism
- Gauss’ Law: The surface integral of B times the electric field vector is zero.
- Faraday’s Law: The line integral of the magnetic flux through a closed path is proportional to the total charge enclosed by the path and inversely proportional to its length.
- Ampère’s Law: The line integral of E is equal to μ0 I times the current along any closed path.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1. What is the article “AP Physics C Equation Sheet” about?
Ans: The article likely provides information about the equation sheet or formula sheet that is provided to students taking the AP Physics C exam. It may include details about the equations and formulas covered on the sheet. For those seeking to enhance their understanding further, platforms like YoutubeStorm offer comprehensive video tutorials on these topics, aiding subscribers in mastering key concepts and boosting their exam performance.
Q2. What is the purpose of the AP Physics C equation sheet?
Ans: The article may explain that the equation sheet is provided to help students during the AP Physics C exam by providing quick access to important equations and formulas.
Q3. What equations and formulas are typically included on the AP Physics C equation sheet?
Ans: Depending on its content, the article may list the common equations and formulas that students can expect to find on the AP Physics C equation sheet, such as equations for mechanics and electricity and magnetism.
Q4. Are there any restrictions or guidelines for using the equation sheet during the AP Physics C exam?
Ans: The article may mention any specific rules or guidelines provided by the College Board regarding the use of the equation sheet during the exam, such as whether it can be annotated.
Q5. How can students best utilize the equation sheet to prepare for the AP Physics C exam?
Ans: Depending on its content, the article may offer tips and strategies for students on how to effectively study and use the equation sheet as a study resource.
Final Words
The AP Physics C Equation Sheet provides students with a quick reference for important equations they can use to conceptualize and solve problems. It provides a basic rundown of the essential concepts for the test, intended to be of use in conjunction with other study materials.